Other Terms
| Bather capacity | The maximum number of bathers permitted in a swimming area. | |
| Beach | A beach is one form of waterfront, often characterised by a sloping shore along a body of water that is washed by currents, waves or tides and covered by sand, mud or gravel. Beaches are common access areas to inland waterways for users. In the context of an inland waterway, a beach may also be constructed from concrete or similar, or simply covered by grass. The key aspect of what constitutes a beach is how the area is used by recreational users.
| |
| Channel | Means the width of the waterway at a particular point.
| |
| Coastal waterfront | Includes beaches (bay and surf) and other constructed waterfronts with direct access to ocean waters. Can be exposed to ocean swell, currents, rips, strong winds or surf, or can be a bay, harbour or estuarine environment. | |
| Drowning prevention | Defined as a multidisciplinary approach that reduces drowning risk and builds resilience by implementing evidence-informed measures that address hazards, exposures, and vulnerabilities to protect an individual, community or population against fatal and non-fatal drowning. | |
| Exposure | The impact a hazard may have on a person or thing. Exposure is a continuous variable which means it can increase or decrease by presence, number, time or frequency. | |
| Foreshore | The area of land that borders a body of water, such as a river, lake, or ocean. It encompasses the land that lies between the water's edge (waterfront) and the first line of natural vegetation or development. The foreshore area can include beaches, cliffs, dunes, and other features that are influenced by the water body. It is a significant and ecologically sensitive zone, and its management is crucial for maintaining environmental balance and providing access to waterways. | |
| Hazard | A source of harm to a person or property. | |
| Instructional swimming | Programs conducted for the purpose of teaching swimming and water safety. It does not apply to water activities such as recreational swimming, surfing, canoeing, boating etc.
| |
| Lifeguard | A person designated by the owner or operator to supervise and maintain the safety of waterway users. Lifeguards are primarily engaged to prevent and respond to emergency situations. | |
| Lifeguarded waterfront | An area designated for swimming where trained personnel provide an emergency response service to first aid, water rescue situations and public education to bathers. | |
| Lifesaving programs | Lifesaving in its broadest context implies the saving of life through the prevention of accidents, personal survival and the rescue of others (e.g. the Bronze Medallion). | |
| Operator | A person or entity designated by an owner as being responsible for the operation of the waterway, or its waterfront and associated facilities. Refers also to tourism, camping, recreation, boating, swimming or program operators, accommodation providers with waterfronts, private businesses on waterfronts such as bars and restaurants and event and festival operators where waterways or waterfronts are used. | |
| Owner | A person or entity who owns a waterway, waterfront or the access to a waterway such as a national, state or local government, private landowner, statutory authority, business, camp owner or private corporation. | |
| Patrolled area | A routine or planned inspection and monitoring activity carried out within a designated area. Patrols can be constant or intermittent. Patrols can be at a designated patrolling location, or can encompass a larger area, such as a park or protected reserve. During a patrol, preventative actions are taken to ensure compliance with regulations, address any potential issues, and help or information to visitors. Patrols can help maintain the natural area’s integrity, safeguard its natural resources, and ensure the safety and enjoyment of visitors. | |
| Recreational swimming | Structured or unstructured activities in water for the purposes of leisure, fitness or fun. | |
| Risk | The effect of uncertainty on objectives or of a harm occurring as a result of a hazard. | |
| Risk appetite | The amount of risk an entity is willing to accept or retain in order to achieve its objectives. | |
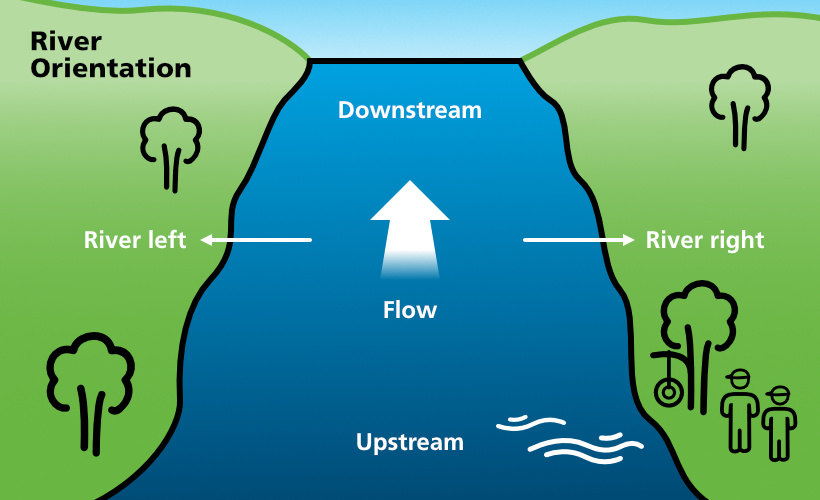
| River Orientation: | A consistent approach to orientation in a moving waterway, whereby directions are always given from the perspective of the individual facing downstream. There are 4 basic directions:
Figure 1: River Orientation
| |
| Scanning | Continuous observation of a place, person, group, or ongoing activity in order to gather information. | |
| Supervision | The systematic process for monitoring, ‘watching over’, a waterfront to maximise the safety of patrons and prevent injury or death. | |
| Swimming area | A section of the waterfront or waterway marked and designated exclusively for swimming and wading activity; free of hazards that pose a risk to the safety of users; in which boating is prohibited. | |
| Vessel | Any type of watercraft, including non-displacement craft used, or capable of being used, as a means of transportation on water. | |
| Vulnerability | Describes attributes of the subject of the risk, which may be an individual, community, asset or systemic. | |
| Waterfront | The area of land adjacent to the waterway by which access to the waterway is made available. | |
| Water course | The direction of the flow of moving water and the characteristics of the construction and/or composition of the waterway at a particular point. |